On this page
Connect to Postgres
This tutorial covers how to connect to a Postgres database from an application deployed on Deno Deploy.
You can find a more comprehensive tutorial that builds a sample application on top of Postgres here.
Setup Postgres Jump to heading
This tutorial will focus entirely on connecting to Postgres unencrypted. If you would like to use encryption with a custom CA certificate, use the documentation here.
To get started, we need to create a new Postgres instance for us to connect to. For this tutorial, we will be using Supabase as they provide free, managed Postgres instances. If you like to host your database somewhere else, you can do that too.
- Visit https://app.supabase.io/ and click New project.
- Select a name, password, and region for your database. Make sure to save the password, as you will need it later.
- Click Create new project. Creating the project can take a while, so be patient.
Gather credentials from Postgres Jump to heading
Once you've set up your Postgres database, gather your connection information from your Postgres instance.
Supabase Jump to heading
For the Supabase instance above, to get your connection information:
- Navigate to the Database tab on the left.
- Go to the Project Settings >> Database and copy the connection string from the Connection String >> URI field. This is the connection string you will use to connect to your database. Insert the password you saved earlier into this string, and then save the string somewhere - you will need it later.
psql Jump to heading
If you are using psql, you should generally be able to find your connection information by running:
test=# \conninfo
Your Postgres connection string will take the form:
postgres://user:password@127.0.0.1:5432/deploy?sslmode=disable
Create a project in Deno Deploy Jump to heading
Next, let's create a project in Deno Deploy and set it up with the requisite environment variables:
- Go to https://dash.deno.com/new (Sign in with GitHub if you didn't already) and click on + Empty Project under Deploy from the command line.
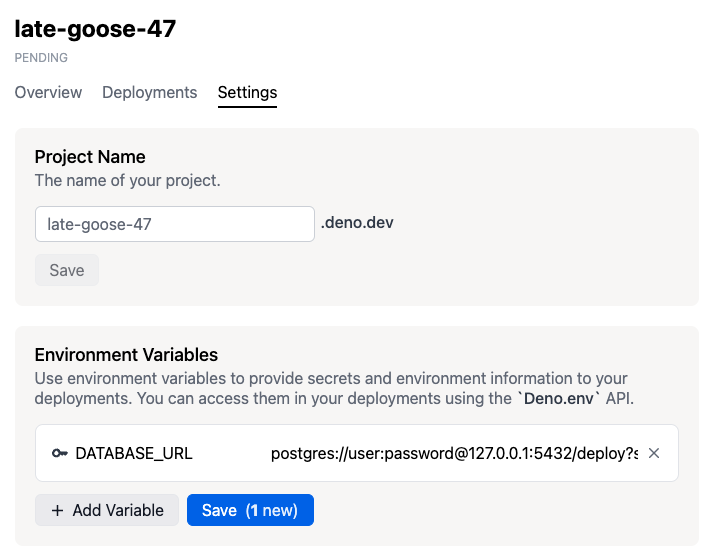
- Now click on the Settings button available on the project page.
- Navigate to Environment Variables Section and add the following secrets.
DATABASE_URL- The value should be your connection string that you retrieved in the last step.
Write code that connects to Postgres Jump to heading
To read/write to Postgres, import the Postgres module, read the connection string from the environment variables, and create a connection pool.
import { Pool } from "https://deno.land/x/postgres@v0.17.0/mod.ts";
// Get the connection string from the environment variable "DATABASE_URL"
const databaseUrl = Deno.env.get("DATABASE_URL")!;
// Create a database pool with three connections that are lazily established
const pool = new Pool(databaseUrl, 3, true);
// Connect to the database
const connection = await pool.connect();
try {
// Create the table
await connection.queryObject`
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS todos (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
title TEXT NOT NULL
)
`;
} finally {
// Release the connection back into the pool
connection.release();
}
Deploy application to Deno Deploy Jump to heading
Once you have finished writing your application, you can deploy it on Deno Deploy.
To do this, go back to your project page at
https://dash.deno.com/projects/<project-name>.
You should see a couple of options to deploy:
- Github integration
deployctldeployctl deploy --project=<project-name> <application-file-name>
Unless you want to add a build step, we recommend that you select the Github integration.
For more details on the different ways to deploy on Deno Deploy and the different configuration options, read here.
Help us make these docs great!
Make a contribution
Deno's docs are open source. See something that's wrong or unclear? Submit a pull request:
Edit this page